AD Converter PCF8591 for Raspberry Pi: Difference between revisions
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
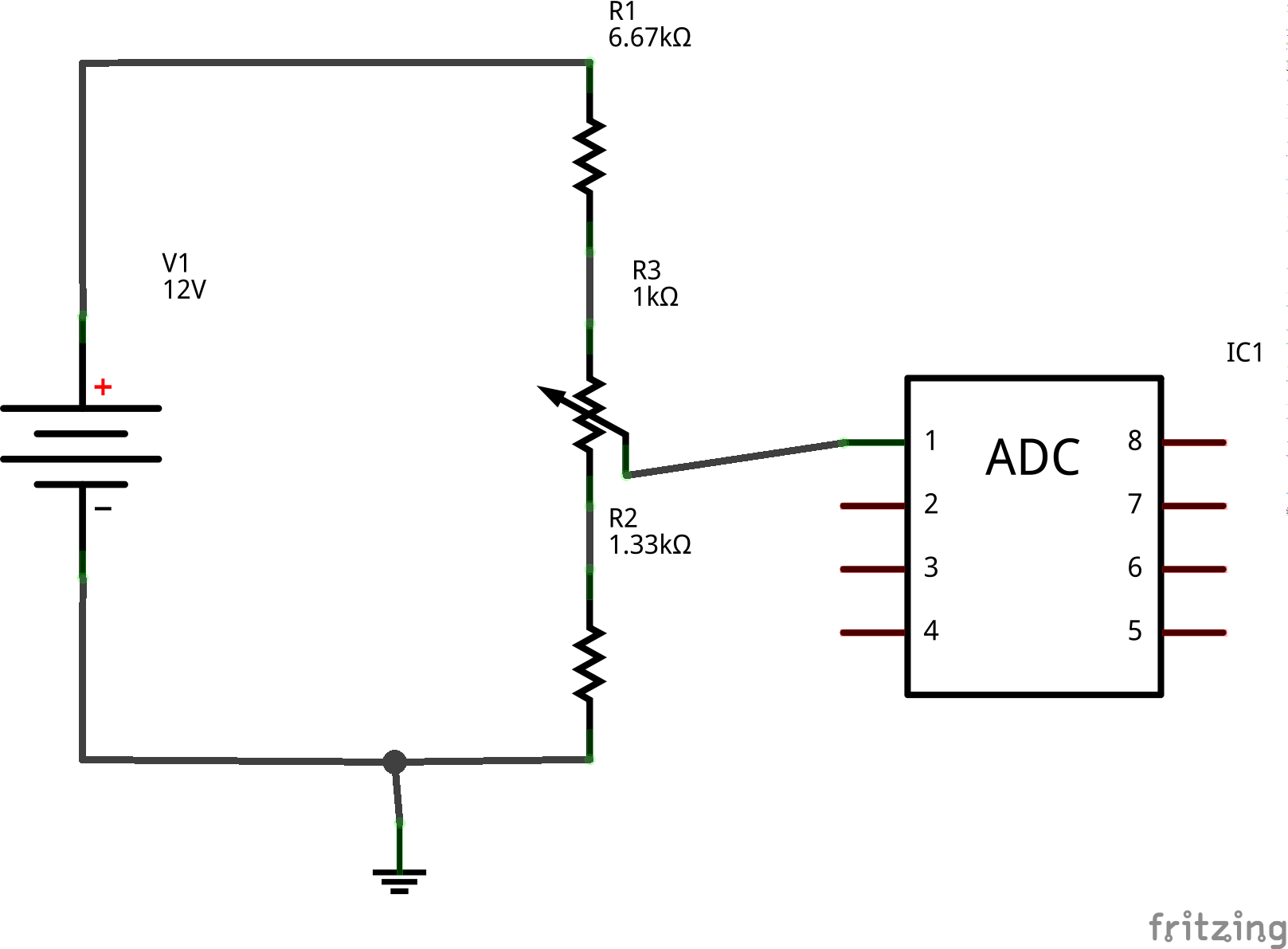
[[File:Voltage-divader.png|600px|Simple voltage divider connected to ADC]] | [[File:Voltage-divader.png|600px|Simple voltage divider connected to ADC]] | ||
[[File:Adc.jpg|400px|Calibrating ADC with voltage divider using voltmeter]] | |||
Revision as of 12:47, 21 March 2015
Under construction
Intro
Have you ever wondered how to measure battery voltage with Raspberry Pi? Do not wonder more. You can simply use ADC converter for 2 USD on Ebay with product name PCF8591 and connect it using I2C to your Raspberry Pi.
How it works?
Basically AD convertor take Vcc voltage as reference, measure input voltage to this reference and output number of how many percent of reference voltage is input voltage. Eg. if you use Raspberry Pi and provide Vcc at 3.3V and input voltage would be 3.3V, output from ADC would be 1.00. If input voltage for same reference would be 1.65V, output from ADX would be 0.50 (input voltage is half of reference voltage).
But usually we need to measure higher voltages than 3.3V. For example in my case I need to measure Lead-Acid battery which provides voltage between 11-14V. So how to solve it if the reference voltage is only 3.3V and anything higher would not be able to be measured. In this case we use voltage divider (see image below) which divide input voltage 6 times. So for example for 12V output voltage would be 12V/6 => 2V and this could be measured. We can easily get input voltage on Raspberry Pi using simple mathematical operation percentage * 3.3V (Vcc) * 6 (divider) and now we will get 12V again on screen.
As you can see on image below I use trimr and voltmeter to calibrate AD converter with computer.